MONAURAL / BINAURAL BEATS AND BRAIN STATES
by Marco Stefanelli
In recent decades, the
use of pure tones for entrainment (brainwave entrainment) has
become very popular especially with binaural beats, largely thanks
to the research of the Monroe Institute and the
relative products Hemi-Sync.
In fact they have become so popular that many people have the
impression that "Binaural Beats" is just another way of defining
the cerebral inductions.
But so it's not because the technique of binaural beats is
currently only one of the various techniques of induction and in
fact there are other techniques that use the beats with pure tones
such as the "Monaural Beats" and "Harmonic Box X".
The binaural beats are therefore the sound pulses produced by two different sounds and separated for the two ears (stereo), unlike the monaural beats that instead can also use a single channel, and therefore a single ear (monaural).
The beat is said to monaural when the two sounds
are coming in one ear or both, previously mixed in the air; is said
binaural when, through two separate acoustic diffusers, in such a
way that a frequency arrivals to one ear and the other to the
second.
From the physiological side, the two phenomena are clearly different: the first one is born from not intrinsic linearity of the cochlea, the second, perceptible only for frequencies of sounds components not exceeding to about 1500 Hz, is a central phenomenon clearly temporal.
In acoustics, is called beat, the external physical phenomenon which determines the monaural beat, namely the composition or interference in time,of two pure tones of equal amplitude, but of slightly different frequency.
In the more general case, we speak in physical of phenomena beat every time that overlap two sound waves, optical, electromagnetic, of same amplitude and frequency slightly different.
If the two waves have
frequencies f1 and f2 and amplitude A, the resulting wave has an
amplitude variable between 0 and 2 A and a frequency equal to (f1 +
f2) / 2 and the frequency of the perturbation, or beat, equal to
the difference between the frequencies components.
In the case of electromagnetic waves, the two frequencies may
also be generically little different, with reference more to their
relationship, which may be, for example, equal to 0.9, that the
value of their difference.
The
Binaural beats are of beats or rhythmic beats
sound carried by two sounds (Pure Tones) differents, low-intensity
and separated for the two
ears.
When a tone is listened with an ear, and another slightly different tone is listened in the other ear, the brain produces a third tone that pulsates at the frequency of the difference between the two tones.
For example, if
a
1000 Hz tone
is subjected
in his
left ear
and
a
tone
of 1010
Hz
is subjected
simultaneously
to the right
ear,
a third
tone
of
10 Hz
is processed and
perceived
by the brain.
Is one of the most popular techniques when it
comes to cerebral inductions or brainwave entrainment and obviously
only works with stereo sound and then it's recommended to use
stereo headphones, unlike the method brother Monaural
beats.
The Monaural beats are similar to the Binaural beats with the difference that the two tones carriers are mixed before being sent to the ear. When two slightly different tones, suitably twisted into a single sound at low intensity, are subjected to the same ear, the brain processes and perceives a third tone equal to the difference of the two tones heard.
Is a technique
highly effective and does not require the use of stereo headphones.
Given the complexity of the information and we will try to provide simple explanations, but also scientific and technical information most complex supported and complemented - where possible - from images, graphics and animations.
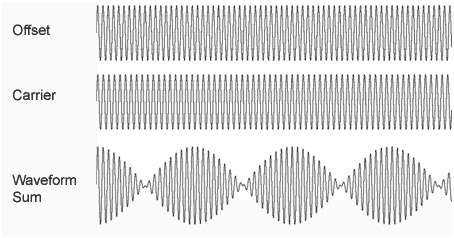
The monaural and binaural beats are the result of the sum of two waveforms which are so close in frequency to be perceived as a single pulse or beat.
The lower tone is called "carrier" (or vector) while the highest is called "offset".
The binaural beats are auditory brainstem responses which originate in the superior olivary nucleus of each cerebral hemisphere.
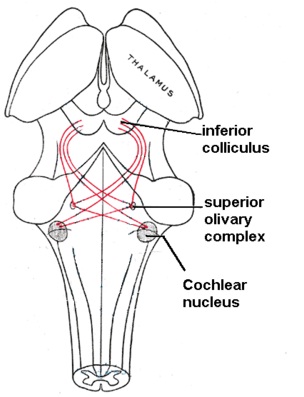
This is because the brain has to rework the tones and binaural beats using a different part of the brain compared to monaural beats.
This is the reason why the technique of binaural beats is unique and special in comparison to other methods of induction.
In order to produce binaural beats, the brain must be able to identify the phase angle between the two tones.
Unfortunately the cerebral apparatus has difficulty in identifying the phase relations with frequencies above 900 Hertz, so that at higher frequencies the binaural beat becomes imperceptible although still effective up to around 1500 Hz.
When the difference of the frequencies of the two tones is over at 25 Hertz, the brain is not unable to determine the phase relationship between them, so that the two tones are perceived as separate in contraposition to the beats combined.
Even when the brain produces binaural beats, the modulation depth and much lower than the monaural beat.
This is the reason for which it is often difficult to perceive binaural beats even at 440 Hertz, which is the optimal frequency of detection.
These are the limitations of a normal human brain, a brain that suffered neurological damage may not be able to perceive the binaural beats.
Unlike monaural beats, binaural beats maintain the full effect even if the two tones are of different amplitude and can be used even if the carrier is below the threshold of human hearing.
In this case the effect is however minor.
Unfortunately, the binaural beats produce only small evoked potentials in the auditory cortex of the brain that is responsible for the BWE (brain wave entrainment).
A study by Dale S. Foster in 1990 concluded that although the binaural beats produce BWE, they would not be significant enough in themselves.
In his study a sound generated artificially produces more alpha waves of a binaural beat of 10.5 Hz.
They can be very hypnotics, this is mainly due to the Ganzfeld effect, which is a state of reduced sensory stimulation, usually produced by covering the eyes of a subject lying, with two half ping-pong balls, on which is aimed a red light, and spreading through a pair of headphones the white noise.
Since that require the use of both hemispheres of the brain, the binaural beats can also induce cerebral synchronization, "whole-brain effect", which is an effect boasted by The Monroe Institute (TMI) and by others who have given of proper names to their products.
Nevertheless, other forms of induction, such as meditation itself, can produce hemispheric synchronization.
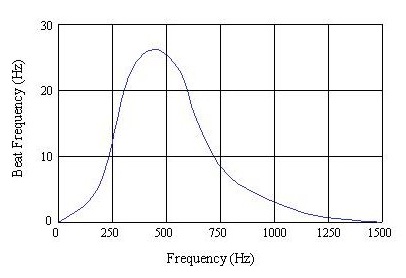
He recommends the use of carrier frequencies between 200 and 1000 Hertz, with greater effectiveness at around 500 Hz.
Obviously, these recommendations are not obligatorily applicable to monaural beats, but can be used to get best results.
The Dr. Tom Budzynski has studied the use of two binaural beat frequencies contemporarily and concluded that the brain can not perceive two frequencies simultaneously.
A single binaural beat plus a light stimulation instead could be perceived simultaneously.
However, many organizations and research centers recommend the use of a dual binaural beat.
James Mann has discovered the technique "Harmonic Box X" that utlilizza 4 entries (2 for ear) and uses their harmonics between them for particular inductions.
This is a very effective method, but only because it uses the monaural in addition to the binaural beats.
As we said, the monaural beats are elaborate by a different area of the brain compared the binaural beats, so it is possible to induce two or more frequencies using monaural beats in association with the binaural beat and eventually at light stimulations.
Anyway it seems is not possible to induce two or more frequencies simply using two or more sets of binaural tones.
Final Thoughts:
- To use binaural beats is advisable to use a carrier frequency of about at 440 Hz;
-
You can use
the binaural beats only if the difference between the two
frequencies is less than 25 Hz;
- Don't use more than 2 sets of binaural beats and only one if is not provided the association with monaural beats;
- The monaural beats are not reprocessed by the brain whereby do not suffer from the limitations of binaural. They are produced at any frequency beyond 900 Hz and can be perceived even if separated by more than 25 Hz;
- The monaural beats have the disadvantage that in order to preserve their effectiveness, both tones must have the same amplitude. Secondly the tones must have a high volume so as to enable an appreciation of the modulations of tones;
- Despite their limitations, the monaural beats are very effective in producing inductions and also have the advantage of being hypnotics such as when are listened through headphones.
What are in practice the frequencies "Binaural Beats"
If a steady tone of 434 Hz (1 Hz = 1 pulse for second), is applied to the left ear, and another steady tone of 454 Hz is applied to the right ear, the difference of 20 Hz will be perceived by our brain; and this will stimulate him in several ways.
Frequencies
"Binaural
Beats",
discovered in
1839 by
German
H.W.
Dove and
tested on the
brain
by Dr.
Gerald
Oster
in 1973 at
Mount
Sinai
School of
Medicine in
New
York,
are the
application
of these differences
in
frequency
between
one ear
and the other
, so
that the brain
is stimulated
positively.
These
can
stimulate it
in
different ways,
facilitating
relaxation, learning,
meditation, sleep, and many
other aspects of
life.
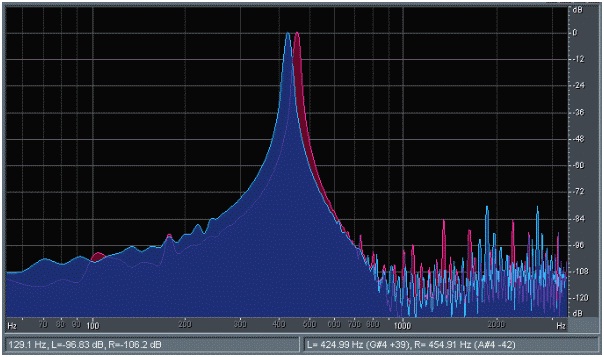
Figure
1
- Frequency analysis of binaural
beat
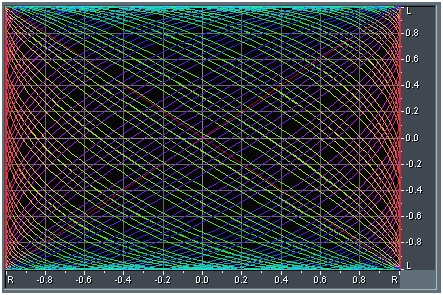
Figure 2 - Phase Analysis of Binaural beat - (Lissajous Plot graph)
On the horizontal line we have the left channel and the right channel in the vertical. Notice how the "field" stereophonic audio is harmonically and fully distributed.
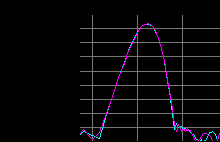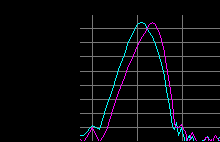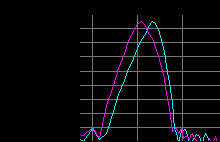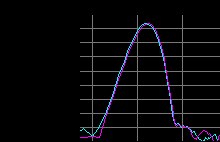
Figure 3 - Frequency Analysis (animated) of Beat (20Hz) in frequency modulation and phase difference.
In figure 3 you can see the frequency analysis (animated) of a beat of 20 Hz (infrasound) generated by the modulation in frequency and difference of phase of a carrier signal audible (400Hz), equal for the left channel (fuchsia) and right channel (pale blue).
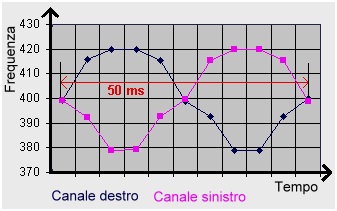
Figure 4 - Chart of Beat (20Hz) in frequency modulation and phase difference (180 °)
The frequency of each channel is between 420 Hz and 380 Hz.
To notice the phase difference of 180 degrees between the two channels with an oscillatory frequency of 20 Hz in a time of 50 milliseconds.
Frequencies and Cerebral States
The result of the track contains, usually, frequencies below 30Hz.
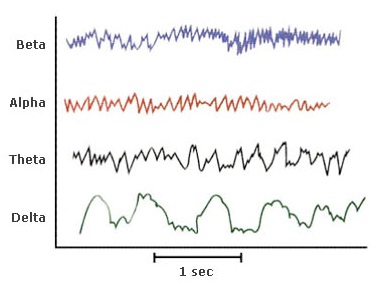
Delta from 0,5 to 4Hz - Deep sleep and coma;
Theta from 4 to 8 Hz - Drowsiness and the first stage of sleep, trance and dream;
Alpha from 8 to 14 Hz - Relaxation vigilant, awareness and integration;
Beta from 14 to 30 Hz - Alertness and concentration;
Gamma - Waves are very rare and related to frequencies above 30 Hz in the range 30-90 Hz and are typical of states of deep meditation and great energy, are correlated with the will and psychic powers, with the concentration and problem-solving.
The dominant frequency in the EEG determines in what state the brain is found, and, if the amplitude of alpha waves is more higher than the others, it is said that the brain is in the Alpha state.
The technology of Binaural Beats by Remo Badoer
It was the German
Heinrich Wilhelm Dove in 1839 to discover that when the sounds of
different frequencies are perceived separately from each ear, the
human mind creates the perception of "beats", a third sound that
does not exist as such but is created individually as perception
inside the acoustic system.
This discovery was neglected until 1973, when Gerald Oster
published in the journal Scientific American an article entitled
"Auditory beats in the brain.
Since the binaural beats are perceived even when the
acoustic frequencies are below the threshold of human perception,
Oster intuited that these beats were to have an effect on the human
brain different from that of the sounds normally perceived: this
effect was that the waves brain were "channeled" in a single
frequency, equivalent to the difference of the frequencies of the
two sounds perceived by the individual ears.
In simple terms, it works like this: if the left ear hears a sound
of 200 Hz (Hertz) and the right ear at the same time a sound of 205
Hz, then the brain waves are channeled in a frequency of 5
Hz.
This
ability to change at will the frequency of brain waves, especially
after the experimental confirmations by EEG (electroencephalogram)
at the Monroe Institute of Applied Sciences, opened a great new
perspective on the applications in the field of medicine in general
and in particular in fields of diagnostics, neurology and
psychiatry.
The human
brain is composed of billions and billions of neurons that
communicate with each other by means of electricity.
This enormous activity can be detected in the form of waves via an
EEG. These waves, called brainwaves are measured in Hertz (Hz) and
were divided into 4 basic types; to each typology corresponds a
particular mental activity.
These are the four basic categories, which correspond to different mental states
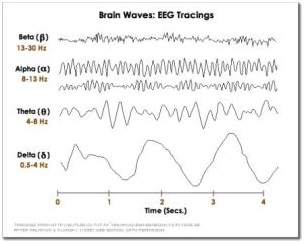
Beta
(frequency
between
13.0 -
40.0
Hz)
This is the
fastest
frequency,
corresponds to the
state
of
normal
consciousness
and is associated with
attention,
the state of
wakefulness, concentration
and physical
activity
and manual;
for
the
majority of people, and in most
of the
time
the
beta brainwaves
are
prevalent
with respect
to the
other.
At the high end
of
this category (above
30 Hz
and beyond
40
Hz) we can
find
states of
discomfort, stress,
anxiety,
neurosis,
etc..
Alpha
(frequency
between
8.0 -
12.9
Hz)
The brain waves in this category are those that accompany
states of deep relaxation and concentration. In the high end of
this category we find states of concentration relative to what can
be called "super learning" while in the low-end we find states of
relaxation as the moments before sleep, light meditation,
introspection, etc.. In a range even more lower, just before of the
category Theta, there are mental conditions associated to the peace
and inner satisfaction.
Theta
(frequency
between 4.0 - 7.9 Hz)
The brain waves
in this category are those of REM sleep (rapid eye movement, the
stage of sleep in which we dream) that have been associated with
high creativity, healing, intuition, deep understanding, lucid
dreams. Usually, this category can be reached in the waking state
only with deep meditation: experiments with EEG have found Theta
waves in Zen monks during their practices. Some psychologists
believe that this state is the door that leads to the
subconscious.
Delta
(frequency
between
0.1
- 3.9
Hz)
The lowest frequency of brain waves, which usually is
achieved only in the stage of deep sleep without dreams or in
trance (even hypnotic); the mind in this state is not active, the
man is in a state of unconsciousness and has no rational control.
There is who hypothesizes that this state is connected to what Jung
called the "collective unconscious."
Naturally,
these categories are
a
simplification
(and not
everyone agrees
on the
amplitudes
of the
frequencies)
and do not
take
into account
that there are
considerable differences
within the same
category,
for example,
a frequency of
between
16
and
22
Hz.
In addition,
there is never a
cerebral activity
with
a
single
frequency, we say that
the mental state
corresponding to a given
category
is identified
when the
majority
of brain waves
fall into that
category.
However, direct our brain waves toward one or another of these categories causes not only a change in our state of awareness, but also to the physical condition, since to the brain activity corresponds a hormonal activity: for example, it was noted that to the frequency of 10 Hz there is release of serotonin (a hormone that promotes sleep and reduces stress), at 4 Hz we have the release of endorphins and other endogenous opioids (substances that inhibit pain) and so on.
And this addressing of the brain waves that brings controlled changes in the mental state of a person can be done just with the technology of the binaural beats.
The sounds are then heard through stereo headphones in a way that to the left ear corresponds a pulse and to the right ear the other.
After about six minutes of continuous listening (the time may vary, person to person), the two cerebral hemispheres process the different sounds, synchronizing on the result of the frequency difference between the two pulses: for example, if we have two pulses one at 200 Hz, the other at 210 Hz, the brain waves will be channeled to the frequency of 10 Hz which corresponds to the level Alpha.
The listening may last from half an hour to an hour but the effects tend to last for a longer period.
It must be said that in most of the uses it is prefer not to use a single frequency difference but several differences, so that we can move from one level to another or from one frequency to another within the same category.
This ability to create altered states of mind but at the same time controlled has divided the science, and to this day neurologists and scientists are divided among critics, according to which this technology does not give good results, and favourable, that see in the use of binaural beats a new resource to use in the field of mental dysfunction.
It must be said that the recent (2006-2007) clinical trials seem to tip the scales in favor of those that are favorable.
Without however be careful to the medical and scientific research, this area is experiencing for the past few years an extraordinary development: in fact, at the Patent Office of the United States are filed more than 171 patents for software and other technologies based on binaural beats for modify in a controlled manner the mental states (as observed by Scirus).
I want to conclude by recalling that the binaural beats, however, are not the only technology able to modify mental states, there are also specific practices of meditation, breathing, yoga or technologies based on visual stimuli (or a set of audio stimuli and stimuli visual), and more.
And then of course there are the real drugs, both those illegal, that the ones you buy at the pharmacy with or without a prescription.
Bibliography
- Owens, J., Marsh, G.R.: Binaural Auditory Beats Affect Vigilance Performance and Mood. In: Physiology & Behavior, 63 (2), p.249-252, 1998
- Autori vari: Binaural beat technology in humans: a pilot study to assess neuropsychologic, physiologic, and electroencephalographic effects. In: Journal of alternative and complementary medicine 13 (2), p.199-206, 2007
- Wahbeh, H., Calabrese, C., Zwickey, H.: Binaural beat technology in humans: a pilot study to assess psychologic and physiologic effects. In: Journal of alternative and complementary medicine 13 (1), p.25-32, 2007
- Autori vari: Use of binaural beat tapes for treatment of anxiety: a pilot study of tape preference and outcomes. In :Alternative therapies in health and medicine, 7 (1), p.58-63, 2001
- Binaural beat induced theta EEG activity and hypnotic susceptibility: contradictory results and technical considerations. In: The American journal of clinical hypnosis, 45 (4), p.295-309, 2003
- Brady, B., Stevens, L .: Binaural-beat induced theta EEG activity and hypnotic susceptibility.In: The American journal of clinical hypnosis, 43 (1), p.53-69, 2000
- Harris, B.: Thresholds of the mind. - USA : Centerpointe Research Institute, 200







